By Micheal Rios, Tulalip News
Raising youth in our technologically advanced society is a challenge for most caregivers technologywho struggle to understand the effects and how to set limits on their children’s screen time. Today’s youth are the first to be raised in the age of the smartphone, and its influence can be felt everywhere.
Smartphones, video games, and digital media have created new headaches for many families. Concepts like sexting, online bullying, video game addiction, and obsessive social media attachment have become common practice among today’s youth. Behaviors as these can often lead to disruptions in school and sleep, anti-social behavior, and depression. For parents and caregivers, the question of how to even begin addressing these concepts with their children seems like a daunting task.
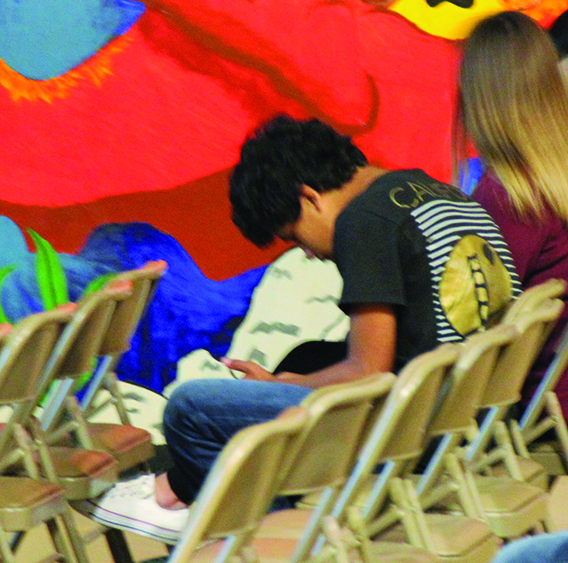
In this context, Tulalip Youth Services invited youth and their parents to participate in a discussion of the topic and view the award-winning film, Screenagers: Growing Up in The Digital Age, on the evening of September 19. Screenagers is the first feature documentary to explore the impact of screen technology on kids and to offer parents proven solutions that work.
“Parents should always take the time to talk to their kids about the risks of technology, especially social media and using technology appropriately,” stated Teri Nelson, Youth Services Executive Director. “There are some great uses in the digital age that provide opportunities to learn and be creative, but with everything there needs to be moderation. I feel big concerns for our youth are online safety, privacy and reputation management with social media. One bad decision to post something inappropriate can have long-lasting, damaging effects.”

During the film’s screening there were 32 youth in attendance, plus several caregivers and Youth Services staff members.
Screenagers provided an in-depth, personal look at how families are coping with kids and screen time, the plot explored how being connected to devices is affecting relationships and even child development. Directed by Dalaney Ruston, a Seattle filmmaker and physician, the movie profiles her own family’s struggles with smart phones, social media, and video games. The film includes interviews with parents, teenagers, authors, psychologists and neuroscientists providing ideas on how we can empower ourselves to best navigate this digital world we live in.
Throughout the film, children and their parents are shown dealing with often serious consequences related to excessive screen time, or screen time without boundaries. Revealing stories that depict messy struggles over social media, video games, academics and internet addiction are shared.
A boy who lives with his grandmother becomes a “different child” when told he has to get off his video games. The grandmother seeks help for dealing with the confrontations.
Another boy, Andrew, is so consumed with playing video games into the wee hours during his freshman year of college that he stops going to classes and leaves school. He enters a rehabilitation facility to treat his addiction.
A girl with a love of photography spends most of her time in her room posing and taking pictures of herself to nurture a social identity aimed at getting “likes.”
Another girl, Hannah, shares a picture of herself in her bra with a boy she likes. When he shares the picture, the girl deals with the fallout at school and being bullied.
It’s not just the kids scrolling Facebook or Instagram or blasting away on the PlayStation that demand the attention of the filmmakers. Adults connected to work and their own social outlets through devices are called out by the very kids who they are attempting to digitally police.
“Can we really tell our kids, ‘Do as we say and not as we do’?” the film asks.
Interwoven into these stories, are cutting edge science and insights from thought leaders who present evidence on the real changes happening in the brain. For example, we are led to believe that through technology we can multitask. However, the truth is our brains aren’t built to multitask. We’re meant to focus on one thing at a time. Switching what’s on our screen from Facebook to Instagram to Twitter and inevitably back to Facebook , that back-and-forth raises levels of the hormone cortisol in our brains. Cortisol is the hormone produced when we are stressed. On top of that, every time you refresh any of your social media feeds, the brief burst of news or images gives you a quick dopamine hit, which activates the brain’s pleasure centers and leaves you wanting more. It’s a destructive cycle that can lead to addiction and an inability to stay unplugged and offline.
While our digital lifestyle is certainly not going anywhere, it’s critical to find a healthy balance between screen time and real-world interactions. In most cases, this means putting realistic restrictions on screen time for children and their parents.
Among community viewers at the film screening was tribal member Nickie Richwine and her three daughters. Following the movie, Nickie shared she already places restrictions on when and how her daughters can use their devices, but has learned additional methods of staying offline from the film.

“My girls are 15, 11 and 8-years-old. I took them all to see Screenagers because as a parent I believe that technology and electronic overuse prevents them from developing social skills that they’ll need as they become young adults,” says Nickie. “Face-to-face interaction is necessary to build healthy relationships with their peers. Texting and IM’ing is no substitute. My kids struggle to understand why I limit their screen time, but one of the main reasons I do is to protect them. Kids don’t understand the internet has a lot of dangers and potentially harmful exposures. I was hopeful that this film would help them understand that.”
Dexter Smith, 8th grader and junior rep for Tulalip Youth Council, was also present for the film and recognized some of his own behavior when it comes to video games. Dexter said he can get too caught up in video games and become angry, especially when he loses. He says he is going to work on that and adds, “I think people my age are on their phones too much when they could be enjoying the outdoors. My advice to youth out here is to stay off of inappropriate sites and not make posts hurtful to others.”
Two young ladies, who wished to remain anonymous, shared, “It’s become way easier to text someone than it is to have a conversation in person. We’re so attached to our phones that we don’t even realize we’re addicted to them. People are controlled by their phones and social media accounts, kids and adults. Even in school kids are constantly posting and updating through their phones during class. It’s a distraction from their education.”
Screenagers: Growing Up in the Digital Age probes into the vulnerable corners of family life, and delves into the messy family conflicts over social media, video games, academics and internet addiction. Only through self-reflection and an open dialogue do solutions emerge on how we can best empower young people to navigate the digital world. More information can be found at screenagersmovie.com.
The doctor’s prescription for limiting screen time
- Dr. Ruston suggests putting phones and other devices away at meal times, in the car and during family outings.
- While studying, teenagers should put their phones in another room but can take “tech breaks”.
- No phones, tablets or other devices in the bedroom when it’s time to sleep.
- Rather than relying on your phone, buy an alarm clock and a calculator.
- Limit interactive video games to certain times – the weekend, for example – especially for younger children.
- Try what a group of teenagers do in the film: when they eat out, they put their phones in the middle of the table. First to check their phone pays for dinner.
- Set aside regular time to calmly discuss any issues about mobile phones and other devices rather than letting them spark arguments.
- Parents worried about their children’s screen usage should think about what they are doing themselves.