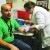
Hernandez has his blood drawn for the A1C diabetes screening. Photo/Micheal Rios
by Micheal Rios, Tulalip News
Despite growing awareness, men usually take a back seat approach to maintaining their health. We will shy away from seeking advice, delaying possible treatment and/or waiting until symptoms become so bad we have no other option but to seek medical attention. To make matters worse, we refuse to participate in the simple and harmless pursuit of undergoing annual screenings.
Enter the Annual Men’s Health Fair held at the Tulalip Health Clinic on December 12. This year’s health fair provided us men the opportunity to become more aware of our own health. With various health screenings being offered for the low, low price of FREE we were able to get in the driver’s seat and take charge of our own health. Cholesterol screening, prostate screening, diabetes screening, and dental screening were among the options for men to participate in. Along with all the preventative health benefits of participating in these screenings, as if that was not reason enough, they gave out prizes and a complimentary lunch to every man who showed up.
At 16.1 percent, American Indians have the highest age-adjusted prevalence of diabetes among all U.S. racial and ethnic groups. Also, American Indians are 2.2 times more likelyto have diabetes compared with non-Hispanic whites (per Diabetes.org). Clearly we are at a greater risk when it comes to diabetes, making it all the more crucial to have glucose testing and diabetes screenings performed on an annual basis. For those men who attended the health fair, they were able to quickly have their glucose (blood sugar) tested with just a prick of the finger.
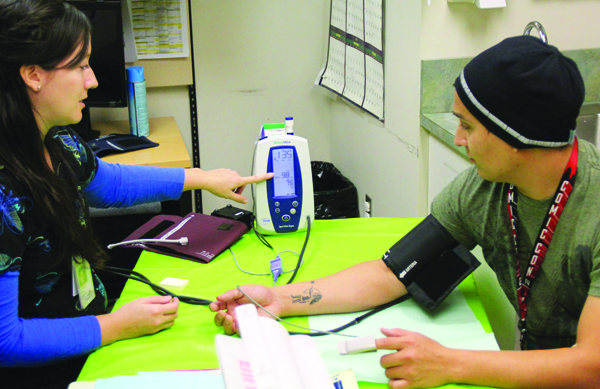
explained. Photo/Micheal Rios
“The blood glucose test is a random check. Random is good, but doesn’t give you all the information which is why we do the A1C testing. It’s just nice to know if you are walking around with high blood sugar. This is a good way of saying ‘Hey, you need to go see your doctor.’ It’s not a definitive diagnosis,” said Nurse Anneliese Means of the blood sugar test.
Taking diabetes awareness one step further, an A1C test was available, by way of a blood draw that would also be used to test for high cholesterol.
“A1C is a diabetes screen. A1C is more of a long term indicator of glucose control as opposed to a regular blood glucose screening, which is here and now. A1C tells you what your blood glucose has been doing for the past 3 to 4 months,” states lab technician Brenda Norton.
How often should we have a diabetes screening performed? “Everyone should be checked once a year,” Norton said.
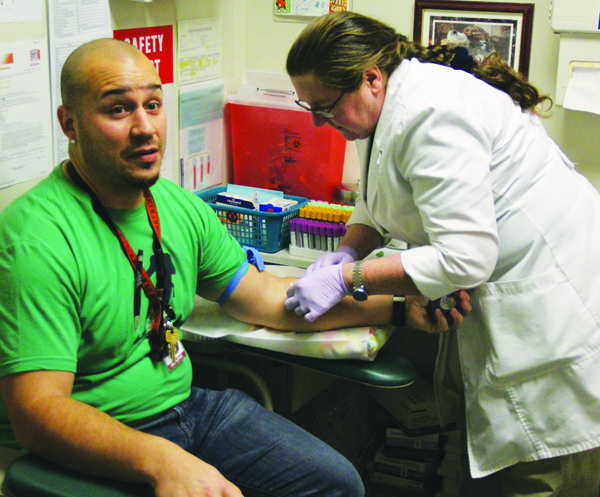
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), heart disease is the first and stroke the sixth leading cause of death among American Indians. High blood pressure is a precursor to possible heart disease and stroke. High blood pressure is also very easily detected by having routine checks of your blood pressure taken periodically.
Nurse Tiffany Lee-Meditz states, “Measuring your blood pressure basically gives us a non-invasive look at your heart health. It can tell us if your heart is too large, if its beating too fast, if its pumping enough blood for the flow to get to all of your tissue and organs, and it can tell us if we need to look further. It can also tell us the health of your vasculature or your vessels, and if we need to look further into that.”
Along with the various health screenings being offered there were information booths available that ranged from alternative health care options in the local area, ways to have cleaner air in your home, and methods to change eating habits as to live a heathier life. There was a booth where we could have our grip tested, a method used for assessing joint and muscle fatigue. Another booth offered us the opportunity to have our BMI (body mass index) and body fat percentage measured. Wondering if you need to cut back on those weekend treats? Or if you need to start leading a more active lifestyle? Well if that BMI was too high and you didn’t like what your body fat percentage was, now you know the answer.
Face it, as we get older, we all need to become more aware of the inevitable health concerns that may one day affect us. The possibility of having to deal with high cholesterol, high blood pressure, diabetes, or the possibility of prostate cancer looms over us all. The only way to avoid such health concerns to heighten our awareness of these preventable conditions. Health educators empower us to be more proactive about our health by getting annual screenings, detecting issues early, as well as seeking medical treatment before a simple, treatable issue becomes life altering.
Photo/Micheal Rios
To all of the men who attended the Men’s Health Fair, Jennie Fryberg, front desk supervisor for the Tulalip Health clinic, issued the following statement, “Again thanks for all the men that came out today. Thanks for taking care of your health, and thanks for the staff that helped me today and made today a huge success for our men. Thanks again.”