
Photo by K. O’Connell 2013
By Monica Brown Tulalip News Writer
TULALIP, WA-Wetlands are widely agreed to be some of the most beautiful places on Earth, with an array of wild and plant life that spark joy in the hearts of many.
“For many of us, water simply flows from a faucet, and we think little about it beyond this point of contact. We have lost a sense of respect for the wild river, for the complex workings of a wetland, for the intricate web of life that water supports.” -Sandra Postel, founder and director of Global Water and Policy Project, author of “Last Oasis: Facing Water Scarcity”, 2003.
Wetlands can be considered the hub of life, where land and water meet you will find an overabundance of life flourishing. Currently most wetlands are threatened with rising sea levels, pollutants and development.
A recent study conducted by Restore America’s Estuary, on the Snohomish estuary, begins to pinpoint the essential need for healthy estuaries and their link to global health. For the study, soil samples (from Smith Island, Spencer Island and Qwuloolt to name a few) were taken in order to establish a count of CO2 emissions that are captured and stored within estuaries that vary in health condition.
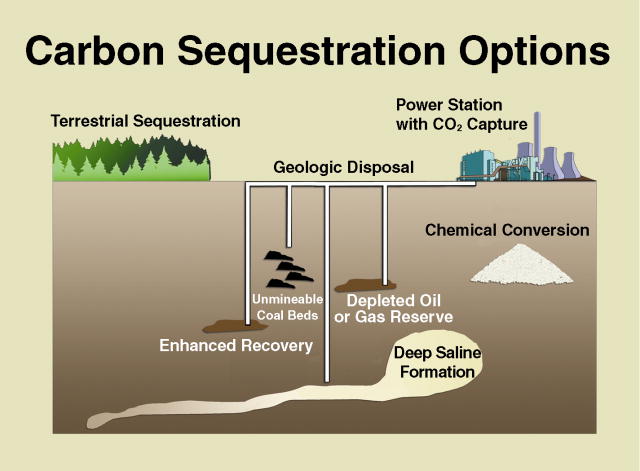
There are numerous ways to remove carbon emissions, most are natural and work through plant life such as forests while others are less natural and work through power plants that capture CO2 and bury it back into the earth or ocean. Coastal wetlands have been labeled as Blue Carbon sequesters and have been found to greatly reduce atmospheric CO2 emissions. Throughout the USA, tidal marshes, tidal forests, saltmarsh grasses, seagrasses, and the mangroves along the Gulf Coast are more effective at sequestering carbon (up to a 100 times faster) and are able to store it for longer periods of time as compared to forests.
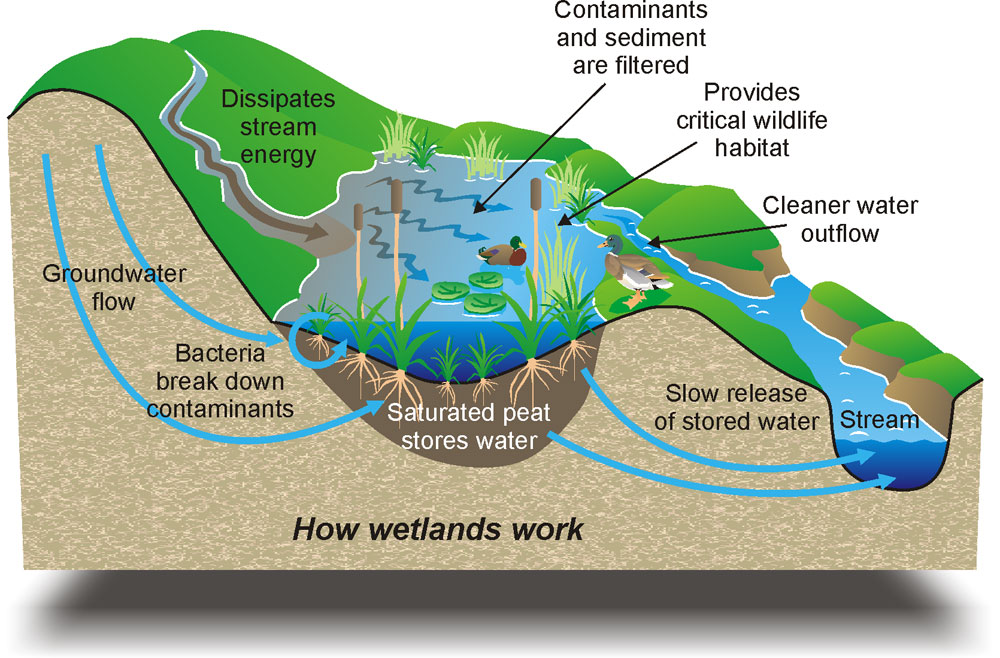
“This report is a call to action. We need to invest more substantially in coastal restoration nationwide and in science to increase our understanding of the climate benefits which accrue from coastal restoration and protection efforts,” said Emmett-Mattox, Senior Director for Restore America’s Estuaries and co-author on the study. “Sea-level rise will only make restoration more difficult and costly in the future. The time for progress is now.”
Through this study a blue carbon working group can be established which will focus, for years to come, on restoring and monitoring Pacific Northwest region coastal wetlands in order to continue collecting and analyzing data which will help to influence better-quality land management, update policies that could one day apply to wetlands nationally.
Due to human impact, coastal wetlands are disappearing at a rapid rate, “at current conversion rates, 30–40% of tidal marshes and seagrasses and nearly 100% of mangroves could be lost in the next 100 years.” (Estimating Global “Blue Carbon” Emissions from Conversion and Degradation of Vegetated Coastal Ecosystems.Pendleton et al., 2012). Although, both are time consuming, maintenance of estuaries is more cost effective than restoring and with rising sea levels (estuary health and life depend on average sea levels), estuaries are losing ground and time has become an issue as well. This national loss of wetlands has branded the Snohomish Estuary as an excellent case study for restoration and estimates of carbon storage.
“It is very fitting that we are implementing some of the world’s leading Blue Carbon research here in Puget Sound,” said Steve Dubiel, Executive Director of EarthCorps. “We have always known that wetlands are a kind of breadbasket, thanks to the salmon and shellfish they support. Now we are learning that they are also a carbon sponge.”
“Coastal Blue Carbon Opportunity Assessment for Snohomish Estuary: The Climate Benefits of Estuary Restoration” finds that currently planned and in-construction restoration projects in the Snohomish estuary will result in at least 2.55 million tons of CO2 sequestered from the atmosphere over the next 100-years. This is equivalent to the 1-year emissions for 500,000 average passenger cars. If plans expanded to fully restore the Snohomish estuary, the sequestration potential jumps to 8.8 million tons of CO2 or, in other terms, equal to the 1-year emissions of about 1.7 million passenger cars. In addition to the climate benefits outlined by the study, healthy and restored estuaries act as spawning grounds and nurseries for commercially and recreationally important fish and shellfish species, provide storm buffers for coastal communities, filter pollutants, and provide habitat for numerous species of fish and wildlife, as well as recreational opportunities for hundreds of millions of Americans annually.
