By Ashley Ahearn, KUOW
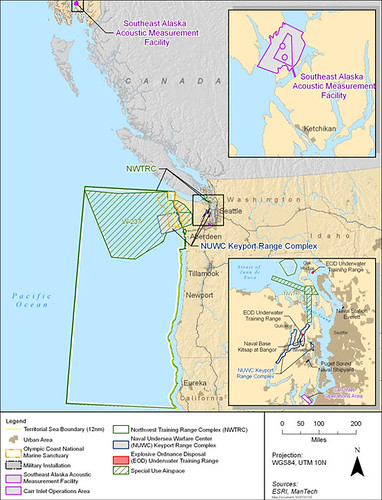
The Navy conducts training and testing in a stretch of the Pacific roughly the size of Montana.
It wants to continue and expand its activities in these waters off the West Coast from Washington to Northern California. But first, the Navy must renew its permit under the Marine Mammal Protection Act.
The plan calls for detonating explosives, moving vessels, and deploying 700 more sonobuoys per year. And that’s drawing criticism from environmentalists who say the increased use of sonar poses increased risk for whales and other marine mammals.
Sonobouys are three-feet-long cylindrical floats are dropped from aircraft into the water. They use active sonar for the audible clues that can help them locate enemy submarines.
“It’s a critical mission for the Navy to be able to identify and locate submarines and utilizing these types of equipment is how we do that job,” said John Mosher, the environment program manager for the Navy in the Northwest.
The Navy says it keeps a lookout for marine life before conducting tests. It estimates that the added buoys will lead to more than 100,000 potential sonar exposures for marine life.
Mosher acknowledge that “exposure numbers” for marine mammals will increase if the Navy gets its way.
“But I’d like to stress that those exposures are at the low level of behavioral disturbance,” he added. “The animals may hear the device but it’s that simple. No injury, no long-lasting impact whatsoever.”
EarthJustice lawyer Steve Mashuda said increased use of active sonar will disrupt marine mammals’ feeding, breeding and calving.
“It’s behavioral disruption, which doesn’t sound bad until you realize this is happening over and over and over again,” he said.
Mashuda said the Navy is increasing the potential risk to marine mammals without increasing the precautions it’s taking to avoid harming them during testing.
Environmentalists takes particular issue with the Navy’s proposal to conduct tests within the Olympic Coast National Marine Sanctuary. It’s an area known to be frequented by blue whales, humpback whales, gray whales and endangered orcas.
“We have been saying for a long time that we’re not attempting to stop the Navy from training,” Mashuda said. “But what we are saying is there are areas on the coast, particularly the Washington coast, where we know that there are higher concentrations of marine mammals.
The Navy did not respond to requests to comment about its need to conduct testing exercises in the Olympic Coast National Marine Sanctuary.
The Navy recently has been criticized by residents of the Olympic Peninsula for proposing to conduct electromagnetic warfare testing in the Olympic National Forest.
Residents of the island communities in Puget Sound report recent increases in loud fighter jets, or “growlers” overhead.
The Navy is expected to release a final environmental review of its proposed marine training and testing activities this summer. The public will have a final chance to comment then.
In preparing that final review, the Navy is holding open house meetingsand taking submitted comments until Feb. 2.
Upcoming public meetings:
Tuesday:
Grays Harbor College HUB
1620 Edward P. Smith Drive
Aberdeen, WA 98520
Wednesday:
Isaac Newton Magnet School Gym
825 NE 7th St
Newport, OR
Friday:
Eureka Public Marina, Wharfinger Building, Great Room
1 Marina Way
Eureka, CA 95501