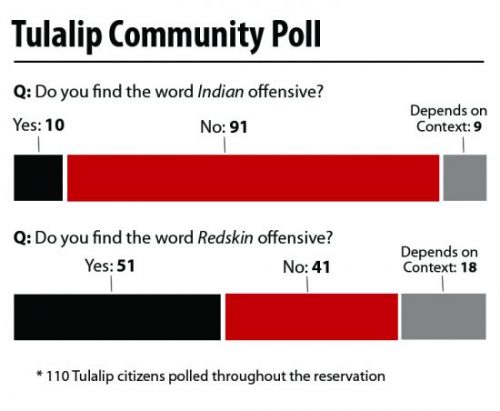By Micheal Rios, Tulalip News
A few days ago the Washington Post, a daily newspaper widely circulated in Washington D.C., published their findings of a poll supposedly showing that Native Americans don’t care that much about the term ‘Redskin’. In fact, the Washington Poll found that an overwhelming 90% of Native Americans weren’t at all bothered by the term. Following their publishing of the poll, news outlets across the country picked it up and ran with it. All the sports related networks, TV shows, talk radio and on-line media were quick to have “Native Americans don’t care about term Redskin” as a major talking point.
Here’s the thing though and it’s a biggie…the Washington Post poll was grossly inaccurate in its methodology. So much so that as a fellow media outlet and news organization, we are embarrassed for them.
“Accuracy is the foundation of good journalism. However, the methodology used to conduct [the Washington Post] poll was fundamentally flawed and as a result, its data set and all conclusions reached are inherently inaccurate and misleading,” stated the Native American Journalist Society in their response to the poll. “The reporting fails to pass the test of accurate and ethical reporting in an example of creating the news rather than simply reporting it.”
The poll was severely flawed on two fronts. First, it relied completely on self-identified Native American respondents in its sampling. So individuals would be asked if they are Native American or not. Then they would be asked if they did claim to be Native, if they were enrolled in a tribe. No research or fact gathering was done to verify whether a respondent was indeed Native or if they were actually enrolled. Secondly, the vast majority of respondents to the poll lived nowhere near a tribal reservation, let alone actually lived on one.
So the Washington Post polled individuals who did not live on or near a reservation and who self-identified as being Native American with no kind of process in place to determine if these people were actually, you know, Native American. Terrible, terrible methodology which led to wide-spread inaccurate reporting in the mainstream media. We can’t begin to assume what every Native American in the country thinks about the word Redskin, but we can figure out what Tulalip thinks about it. While on the subject we also wondered how our people felt about the word Indian. So we did our own poll.
Here’s our methodology. With a quick stop to the Tulalip Admin. Building, Senior Center, Youth Services, Hibulb Cultural Center, Heritage High School, and a few places in between we were able to poll 110 Tulalip citizens. That’s 110 tribal members who are firmly connected to the reservations through residence, school, and work. Of the 110 it was a seemingly 50/50 split of males vs. females, while ages ranged from high school student to tribal elder. It’s interesting to note that every single person polled responded in-person to the polling staff member; no one refused or abstained from questioning.
You may be wondering how a poll of only 110 Tulalip citizens can be indicative of the entire Tulalip Tribe. Well, basically that’s how surveys and polls of nearly any nature work. For example, in the Washington Post poll they used 504 so-called Native people to represent the 5.4 Million Native American population. Here, we are using 110 Tulalips to statistically represent the 2,845 adult members of the Tulalip Tribe.
The polling consisted of two straight-forward questions; 1. Do you find the word Indian offensive? 2. Do you find the word Redskin offensive? Accepted responses were ‘yes’, ‘no’, or ‘depends on the context’. The following is our results.
A whopping 83% of Tulalip citizens said they are not offended by the word Indian, while only 9% said they were offended, and the remaining 8% said it depends on the context.
Now, for the as-of-late, media driven buzz word Redskin: 46% of Tulalip citizens said they are offended by it, 37% said they were not offended by it, and the remaining 16% said it depends on the context. The results were quite mixed, but definitely a far cray from the 90% the Washington Post found to be not bothered by the term. Interesting to note that of the 16% who said it depends on the context, almost everyone said that the context is whether or not a Native or non-Native person was using it.
Interpretation of the results is an entirely different discussion. People can talk about political correctness, media narratives, and social science theories on linguistics and imaging for days on end. That’s not what we are doing at this time. Instead, we just wanted to show what an accurate polling representation of Tulalip citizens would illustrate in regards to the level of offensiveness of two words, Indian and Redskin, on the Tulalip Reservation.
Contact Micheal Rios, mrios@tulalipnews-nsn.gov