
Photo by Peter van Agtmael/Magnum for MSNBC
By Trymaine Lee
05/29/14 MSNBC.com
MANDERSON, South Dakota — In almost any other context it would be a given, an expectation as simple as a dark cloud spitting rain. But when 12-year-old Carleigh Campbell tested proficient on the South Dakota achievement test last year, it was a rather astonishing feat.
Campbell is a student at a school where four students have attempted suicide this year alone. Roughly four out of five of her neighbors are unemployed and well over half live in deep poverty. About 70% of the students in her community will eventually drop out of school.
It’s against this backdrop that Carleigh met expectations on the state’s mandated exam, the only student out of about 150 in her school to do so. To state the obvious, Carleigh’s academic achievement is a bright spot in an epically dark place.
Carleigh is a Native American sixth grader at the Wounded Knee School located on the Pine Ridge Indian Reservation, where a well-documented plague of poverty and violence has festered since the Oglala Sioux were forced onto the reservation more than a century ago. There is virtually no infrastructure, few jobs and no major economic engines. Families are destabilized by substance abuse and want. Children often go hungry and adults die young.
These realities wash onto the schoolyards here with little runoff or relief, trapping generations of young people in hopelessness and despair.
“We’re in an urgent situation, an emergency state,” said Alice Phelps, principal at the Wounded Knee School. “But underneath all the baggage is intelligence, potential, and these children all have that.”
Few communities in America are as eager for a silver lining as the Lakota of the Pine Ridge reservation, situated on more than 2 million rambling acres, nudged up against the Black Hills and Badlands National Park. Nowhere is it more palpable than in the reservation’s schools, a jumble of public, private and federal systems that often overlap but rarely ever bolster the academic prospects of the most forgotten children in America.
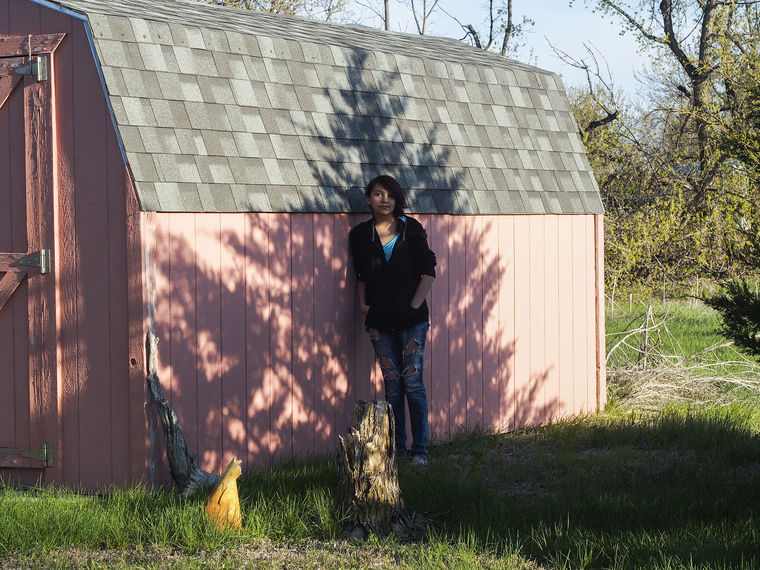

Photo by Peter van Agtmael/Magnum for MSNBC
While the 565 Native American tribes recognized by the U.S. government enjoy sovereign status as separate nations, nearly all Indian education funding is tied up with federal strings. Unlike most public schools that rely largely on local tax money, there are virtually no private land owners on the reservations, so no taxpayers to tax. The government often pays as much as 60% of a reservation school’s budget compared to just 10% of the budget of a typical public school. When last year’s federal sequestration cuts kicked in, Indian country was hit first.
The government is starting to own up to its failures. In a startling new draft report released in April by the federal Bureau of Indian Education, which oversees 183 schools on 64 reservations in 23 states, the agency draws attention to its own inability to deliver a quality education to Native students. BIE-funded schools are chronically failing and “one of the lowest-performing set of schools in the country,” according to the report.
“BIE has never faced more urgent challenges,” the report said. “Each of these challenges has contributed to poor outcomes for BIE students.”
During the 2012-2013 school year, only one out of four BIE-funded schools met state-defined proficiency standards, and one out of three are under restructuring due to chronic academic failure, according to the report. BIE students performed lower on national assessment tests than every other major urban school district other than Detroit Public Schools, the report says.
BIE students also perform worse than American Indian students attending regular public schools. In 2011, 4th graders in the BIE scored 22 points lower in reading and 14 points lower in math on national proficiency tests than their Indian counterparts attending public schools.
BIE schools are typically located in some of the poorest, most geographically isolated regions of the country. Four of the five poorest counties in America are located on reservations. Shannon County, where Pine Ridge is located, is the second poorest with a per capita income of just $6,000-$8,000 a year. It’s also extremely difficult to attract quality teachers willing to relocate to remote outposts with limited quality housing and extreme quality of life issues.
 The BIE blames its failures on “an inconsistent commitment from political leadership,” institutional, budgetary and legal barriers as well as bureaucratic red tape among federal agencies. Those systemic issues have produced a disjointed system that has even clogged up the delivery of required materials, including textbooks.
The BIE blames its failures on “an inconsistent commitment from political leadership,” institutional, budgetary and legal barriers as well as bureaucratic red tape among federal agencies. Those systemic issues have produced a disjointed system that has even clogged up the delivery of required materials, including textbooks.
The BIE has had 33 leaders in 35 years, making a chaotic system that has not operated efficiently for decades even worse.
Dr. Charles Roessel, director of the BIE, told msnbc that the agency is actively consulting with tribes across the country to identify ways the bureau can help tribes bolster the academic outcomes of their students. The draft report was the product of those consultations.
Some challenges are obvious. “How do you get a quality teaching staff at a very remote part of the country where you don’t have a city to support or you don’t have the infrastructure and the salaries are lower?” Roessel said, adding, “The greatest impact in a classroom is the teacher and we need to improve the quality of that instruction. And we have to do it with our hands tied behind our back and our feet tied together, too.”
Never Gave Up Sovereignty
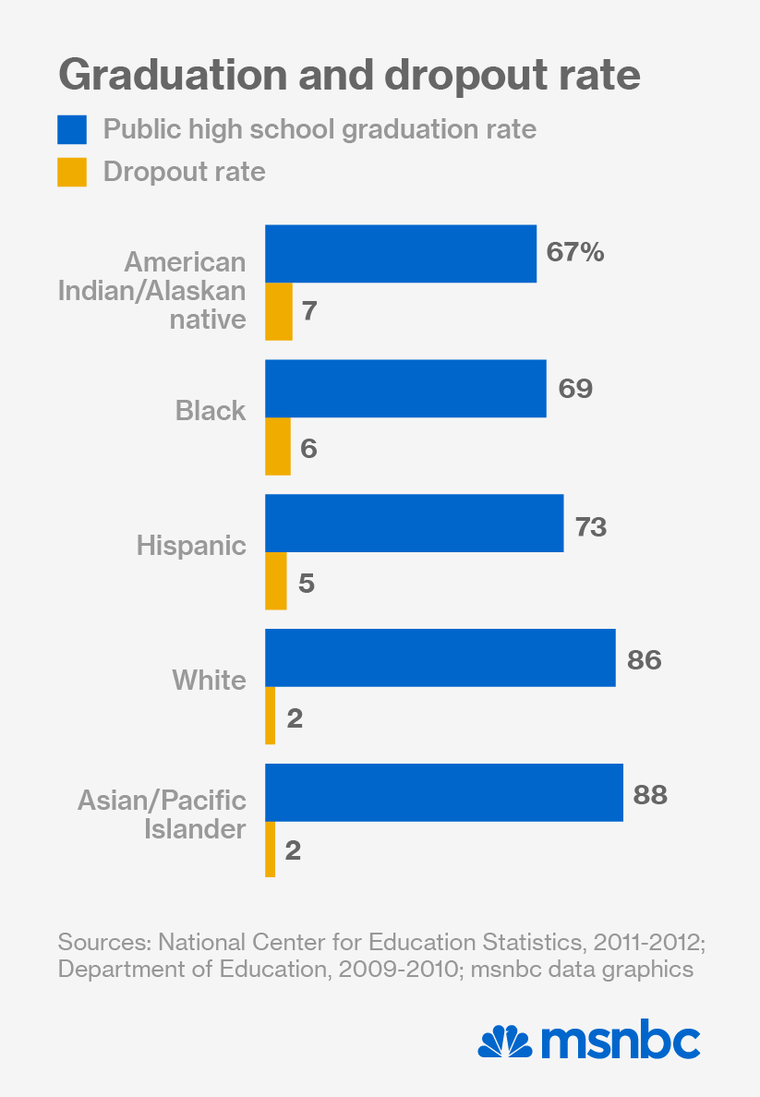
Poor academic performance plagues American Indian students both on and off federal lands.
Even as other historically oppressed minority groups like African Americans and Hispanics have made steady academic progress over the last decade, achievement among American Indian youth has stalled. Huge spikes in black and Hispanic high school graduation rates have pushed the country’s overall graduation rate to an all-time high, while the rate for Native American students is trending in the opposite direction.
Compounding the poor academic outcomes is what advocates in Indian country describe as a history of broken treatises, lingering racism and chicanery.
While tribes operate some of the BIE schools, the funding comes with various restrictions and benchmarks. And in the case of traditional public schools that operate near reservations and have a large number Indian students, funding goes directly to states and does not provide culturally relevant Indian education.
“The central offices, they take their big cut out and they have everything, so by the time it gets to our children there’s very little money left and that’s one of the big problems,” Bryan Brewer, president of the Oglala Sioux Tribe, said on a recent afternoon during a town-hall style meeting between tribal members and BIE officials. “We don’t have enough money for facilities. If we need to buy something, a furnace, something like that, we have to cut out a teacher. It’s that bad.”
The economic and political implications are worst in states with the largest populations of American Indians, including New Mexico, Montana, Oklahoma and South Dakota.
“There are challenging state and tribal dynamics. There’s history involved here and the reality of sometimes incompatible bureaucracies, the lack of capacity and understanding of one another and even alternative goals,” said William Mendoza, the executive director of the White House Initiative on American Indian and Alaska Native Education. “The experience has been one of a history of tragedy where the effort, both real and perceived, was to assimilate American Indians.”
Continue reading article here.
