By Chris Genovall, Huffington Post, Canada
The holidays are a time for celebration as we come together with family and friends for seasonal gatherings or at places of worship. But this time of year should also serve as a time for reflection. We might do well to reflect on whether we will ever achieve “peace on earth” unless, and until, we are willing to extend goodwill and compassion to the non-human inhabitants (i.e. individuals, families, and communities) with whom we share this planet, especially those whose very existence hangs in the balance. Here in British Columbia, that means killer whales.
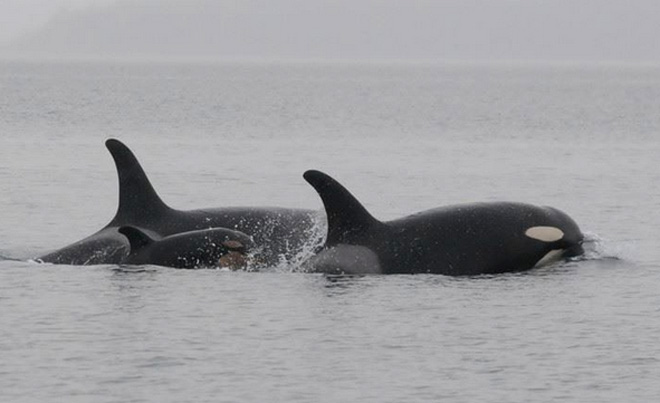
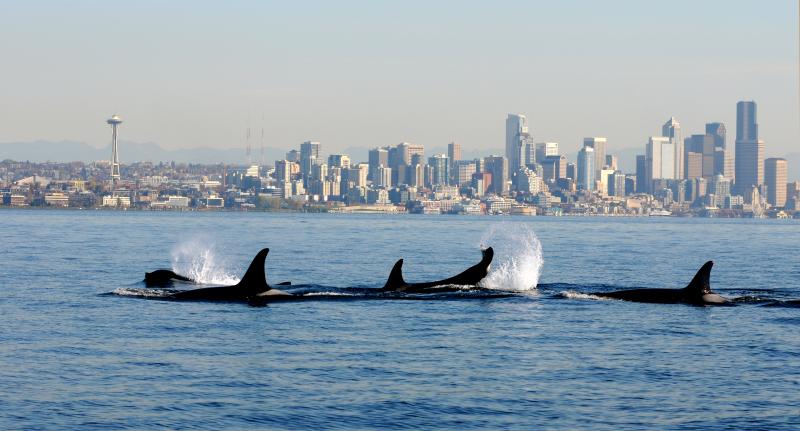
Two distinct populations of resident killer whales reside in B.C.’s waters. The Northern Residents are commonly found on B.C.’s north coast and the Southern Residents within the Salish Sea.
The Northern and Southern Residents differ in population size, population trends, dialects, and importantly, their status under Canada’s Species at Risk Act (SARA). The Northern Residents have a larger, more stable population and are designated as “threatened,” whereas the Southern Residents have an extremely small, declining population, and are designated as “endangered.” Their population has been hovering around 80 since 47 whales were captured and taken for the aquarium trade prior to 1974.
Owing to diminished numbers of Chinook salmon (their primary food), vessel disturbance and underwater noise, pollution, and now facing the pending threat of oil spills, Southern Resident Killer Whales confront a very uncertain future.
Recent viability analysis of their fate by Canadian and U.S. scientists gives them a 50 per cent chance of survival over the next 100 years. Sadly, the population projections for the year 2030 have already been realized, as the number of Southern Residents is now below 80 whales.
The recent death of J32, an 18-year-old breeding female, is a stark reminder of the precipice the Southern Residents stand upon.
Because Southern Resident Killer Whales have been lawfully classified as endangered, the federal government is compelled to implement a recovery strategy that ensures their survival. Yet, the government continues to delay implementation of a credible and comprehensive plan. Their current action plan lacks action, ostensibly because gaps in ecological research are deemed a reasonable excuse for inaction. Twice already, the federal government has lost in court for their failure to act in accordance with science and the law to protect these animals.
After more than a decade of waiting, the Southern Residents are no better off now than when they were listed as endangered 15 years ago. Federal fisheries managers appear unwilling to address the availability of Chinook salmon, an essential food for whales, lest they rile interests in the sports and commercial fishing sectors.
If our grandchildren are to grow up with resident killer whales in the Salish Sea, then crucial decisions need to be made now. For example, an analysis by federal scientists shows that curtailing Chinook fisheries in the ocean can improve the survival rates of these whales. Correspondingly, letting more Chinook salmon spawn could rebuild Chinook runs and provide these whales with the food supply they need.
Federal and provincial governments seem intent on turning critical habitat for killer whales into a shipping corridor for Alberta oil, U.S. coal, and B..C LNG. Moreover, harmful pollutants continue to flow from regional industrial, residential, and agricultural sources into their waters and food. If the National Energy Board knew these whales are unlikely to survive increased tanker traffic – when combined with existing food, pollution, and noise issues – would they be legally compelled to reject Kinder Morgan’s tar sands pipeline and oil tanker expansion proposal?
The federal government’s long-awaited Resident Killer Whale Action Plan finally appeared in 2014. Many had anticipated the plan would include measures to mitigate the hazards confronting the Southern Residents. Alas, the plan failed to include substantive action to reverse what is becoming a grave situation.
But this quandary is not simply a numeric one. Highly intelligent, social, and sensitive, with sophisticated communication skills and very strong familial ties, these whales have an intrinsic right to live their lives.
While the debate regarding the fate of the Southern Residents primarily and understandably takes place in the realm of science, management, and policy, it also brings up issues around ethics, morality, and even spirituality. In fact, I would argue that the matter of what we will choose, or will not choose, to do on behalf of this endangered population of killer whales is, for British Columbians and Canadians, one of the quintessential spiritual decisions of our time.
Having been raised a Catholic, I often times recall the teachings of St. Francis of Assisi. Keith Warner and David DeCosse of Santa Clara University have written that, “St. Francis of Assisi is an example of someone who understood himself to live in a world charged with divine life, in a sacramental world. He was named Patron Saint of Ecologists because he celebrated the beauty and diversity of creation through his prayer and preaching. [In] his ‘Canticle of the Creatures’ Francis sang of all creation as brother and sister. This song is an expression of his moral imagination, because it reflects how he understood himself to live a life of essential kinship with all creation… He viewed the entire created world as members of the divine family… He stands out in Western Christianity as one who lived out a bio-centric vision of the moral life.”
Which brings us once again to the question, if we cannot find the charity in our hearts to allow the Southern Residents to truly recover and regain their rightful place in the coastal ecosystem we both share, then what will that ultimately say about us as a species?
A version of this article previously ran in the Victoria Times Colonist.