All around the United States, people are stepping up to help a damaged planet heal.

By Diane Brooks, Yes! Magazine
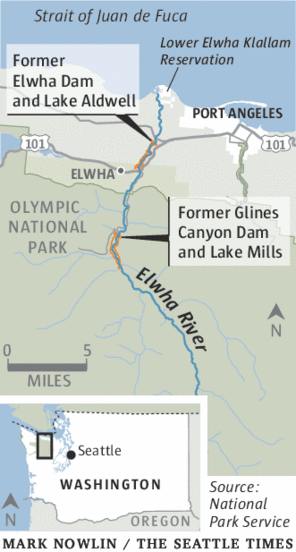
Releasing the rivers
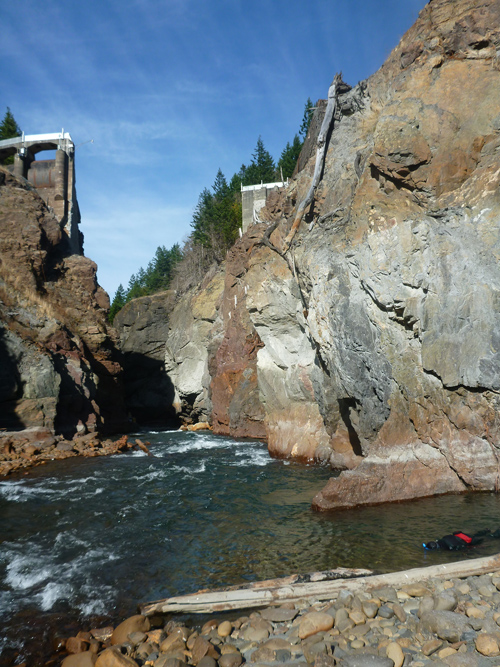
The largest dam-removal project in history reached completion last fall, when excavators dredged the final tons of pulverized concrete from the Elwha River channel in Western Washington. Native fish, banished for 100 years from their historic spawning habitat, already were rediscovering the Elwha’s newly accessible upper stretches. Within weeks of the final explosion in August, threatened bull trout and chinook salmon were spotted migrating beyond the rubble.
“It was a thrill,” said Olympic National Park spokeswoman Barb Maynes. Before the Elwha Dam was built in 1910, the river produced an estimated 400,000 fingerlings per year, a number that dwindled to 3,000 in recent decades. All five native species of Elwha salmon are expected to repopulate the river.
More than 80,000 dams more than six feet high block U.S. waterways, and activists are cheered by the Elwha success story. Two hydroelectric dams once blocked the Elwha; both now are gone. Sediment that was trapped behind them is washing downstream, replenishing habitat. The first 67,000 seedlings (of a planned 350,000) to help restore native vegetation are already planted on the sites of the former dams and reservoirs. A documentary about the project, Return of the River, came out in 2014.

-
Photo by Shutterstock.
Botanical remedies
Headache or back pain? Before you reach for the bottle of aspirin, consider aspirin’s ancient precursor: white willow bark. Or perhaps echinacea to boost the immune system, aloe vera to heal burns, and black cohosh to ease hot flashes.
The trend away from the profit-based pharmaceutical industry toward natural, age-old botanical remedies is beneficial for the environment and wildlife as well as for the humans who take medications. A U.S. Geological Survey study found chemicals from prescription drugs and over-the-counter medications in 80 percent of water samples drawn from streams in 30 states; those waters flow into lakes, rivers, and eventually the oceans.
Alain Touwaide, co-founder of the Institute for the Preservation of Medical Traditions, says pharmaceutical chemists have inverted humanity’s relationship with medicines. “When a sick person used a plant, this person relied on history, the use of the plant over centuries,” he says. Now a researcher starts with a chemical and then experiments to find its uses. Botanical medicine has “an almost philosophical component,” he says, which helps with healing. Users tap into an interactive “sympathy” between humans and the environment, he says.

-
Photo by Paul Dunn.
Citizen turtle remedies
When a community of threatened Hawaiian green sea turtles began hauling themselves from the ocean onto the northern beaches of Oahu to bask and sleep in the sunshine, word soon spread through the island’s tourism industry. Families began plopping children on turtles’ backs for photos and poking, prodding, and pushing turtles back into the surf.
Concerned, the national Oceanic and atmospheric administration (NOAA) launched a “Show Turtles Aloha” campaign in 2005. North Shore residents quickly joined in, and in 2007 they created the nonprofit Malama na Honu (Protect the Turtles) to monitor the beach and educate visitors every day of the year. About 60 trained Honu Guardian volunteers take turns patrolling Laniakea Beach, working three-hour daylight shifts. They educate tourists about the ancient species, ask beachgoers to keep a respectful distance, and collect data for NOAA.
Hawaiian green turtles were listed as a threatened species under the Endangered Species Act in 1978. They’ve made a remarkable recovery since then, and their major nesting beach at French Frigate Shoals was added to the Papahānaumokuākea Marine National Monument in 2006. The number of nesting turtles has grown annually from 67 in the early 1980s to more than 800 today, according to Irene Kelly, NOAA’s regional sea turtle recovery coordinator.

-
Dennis McClung stands inside what used to be a swimming pool in his backyard in Mesa, Arizona. Now it serves as a closed-loop food-producing farm for his family. Photo by Laura Segall.
Swimming pool becomes backyard farm
It’s a typical Mesa, Arizona, suburban subdivision, except for that corner house with a broccoli patch growing on its low-pitched roof. And those goats, chickens, and ducks roaming the backyard, near the solar panels erected above the entryway to that greenhouse planted in the deep end of an old swimming pool. When Dennis and Danielle McClung bought their ‘60s-era home in 2009, they hatched an eccentric but modest plan to make the best of that decrepit, way-past-its-prime pool. Two days after they moved in, Dennis McClung erected his first in-pool greenhouse, intended to provide food for their young family. He had recently quit his job as a Home Depot department manager; his wife was a nurse. “I convinced my wife of my crazy plan, and she went with it,” he says. “We really wanted to live a more sustainable, self-sufficient life, and we thought this was good idea. And it just kept getting better and better, the more we put into it.”
Today their backyard is a mini-ecosystem—McClung calls it a “closed-loop food-producing urban greenhouse”—and their home is headquarters for the Garden Pool nonprofit organization. Its official aim: sustainable food production, research, and education. At night the chickens roost above the pool’s deep-end rainwater pond so their droppings contribute to an aquaponics habitat for tilapia fish. The McClung’s natural water filtration system uses duckweed and solar energy; their organic greenhouse plants are rooted hydroponically, without soil. Pond snails, which probably hitchhiked in on the duckweed, provide calcium for the egg-laying chickens and help manage a pond-sludge problem.
On a typical day, the system provides the couple and their three children with about half their diet, McClung says. That includes veggies and herbs from the greenhouse; apples, citrus fruit, figs, sugar cane, bananas, and pomegranates picked from a 40-tree grove in their side yard; along with eggs and goat milk.

-
Photo by Shutterstock / Holly Kuchera.
Making room for carnivores
When gray wolves were reintroduced to Yellowstone National Park in the mid-1990s, we learned valuable lessons about the critical role of large carnivores in balancing an ecosystem. The impact on the landscape was dramatic. Two decades later, stream banks stripped by booming populations of deer and elk are growing new trees and shrubs, and birds and beavers are returning to the feast. Even the physical landscape has been altered, as returning vegetation stabilizes banks and prevents erosion.
Now a growing movement of scientists and conservationists is campaigning to go further to ensure the health and survival of large carnivores: defining and protecting ancient migration corridors across the continent. a key component of this campaign is educating affected communities about the importance—and practicality—of coexisting with species that traditionally were feared and killed.
In her new book The Carnivore Way: A Transboundary Conservation Vision, Cristina Eisenberg says coexistence with wild predators isn’t just possible: it’s critical. “Carnivores protect biodiversity, which creates ecosystems more resilient to climate change. The climate change crisis we are facing makes it critical for us to help carnivores thrive wherever we can,” says Eisenberg, lead scientist at Earthwatch Institute.
The Wildlands Network has identified two initial priorities for protection. The Eastern Wildway runs 2,500 miles from Florida’s Everglades through the forests of Alabama and along the Appalachian Mountains to the boreal forests and Maritime Provinces of Canada. The Western Wildway is a 5,000-mile corridor stretching from Mexico’s Sierra Madre Occidental to Alaska’s Brooks Range, running along the Rocky Mountains.

-
Photo from Depave.
Asphalt, be gone
Across the nation, activists are organizing work parties to rip up excess pavement in playgrounds, parking lots, and empty lots, replacing it with pervious surfaces such as porous asphalt, block pavers, and greenery of all sorts. The swaths of impervious pavement that characterize our urban and suburban communities, from sprawling shopping malls to ubiquitous cul-de-sac neighborhoods, have vast ecological impacts. Rainwater—which otherwise would soak into the earth and benefit the habitat—is polluted with oil, antifreeze, and pesticides and then diverted into local streams and rivers.
The Portland, Oregon, nonprofit Depave promotes the transformation of over-paved places, such as schools, while engaging and inspiring communities to reconnect urban landscapes to nature. The organization uses community partnerships and volunteer power, and creates educational events, to pursue its goal of nurturing livable cities where people and wildlife can coexist. Since its initial project in 2008, Depave has transformed more than 123,000 square feet of asphalt, diverting about 2.9 million gallons of stormwater from storm drains. Above, the Creston School depaving project last fall.

-
Photo from Rebuild by Design.
Rebuild smarter
The devastation wrought in 2012 by Hurricane Sandy, including 117 U.S. deaths and an estimated $5 billion in damages to greater New York alone, shocked planners and policymakers into fashioning innovative new tactics to protect communities from future disasters. Rebuild by Design, a unique public-private partnership, is identifying and funding ambitious, creative infrastructure improvements in New York, New Jersey, and Connecticut. A contest initiated by the U.S. government already has allotted $930 million to six winning projects, each crafted with powerful community input.
“Sandy exposed physical and social vulnerabilities of the region. It was not built to withstand the forces of climate change, and now we can rebuild it with better foresight,” said Amy Chester, Rebuild by Design’s managing director.
Major philanthropic partners staffed the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development contest, and the project is funded by Congress, along with the Rockefeller Foundation and other private supporters. Design teams worked closely with local residents, businesses, and governments to codesign realistic solutions that carry broad support, Chester said.
In Manhattan, for instance, the community examined how river berms can benefit daily public life. “A wall can be a piece of art; a wall can be a part of a park. A wall should never be something that walls off the communities from the waterfront,” said Chester. One winning proposal: the Big U river fortifications. A 10-mile stretch of Lower Manhattan is to be protected from future storms and rising sea levels with projects including wide, grass-topped berms and rolling hills and bridges, providing new recreational spaces along the Hudson and East rivers.