CREDIT: Science/AAAS
By Becky Oskin, Staff Writer
July 11, 2013
Two new studies of earthquakes near injection wells have seismologists using words rarely heard these days in earthquake science: prediction and warning.
The research has also renewed calls for better seismic monitoring and reporting in regions experiencing man-made earthquakes.
“Shale gas operations have completely changed our energy policy and people are injecting in places they’ve never injected before. If we’re going to do this safely, we need to address the environmental issues, including protecting water supplies and earthquake risk,” said Cliff Frohlich, a seismologist at the University of Texas Institute for Geophysics who was not involved in the new studies.
The two reports appear in today’s (July 11) issue of the journal Science.
Links between injection and earthquakes
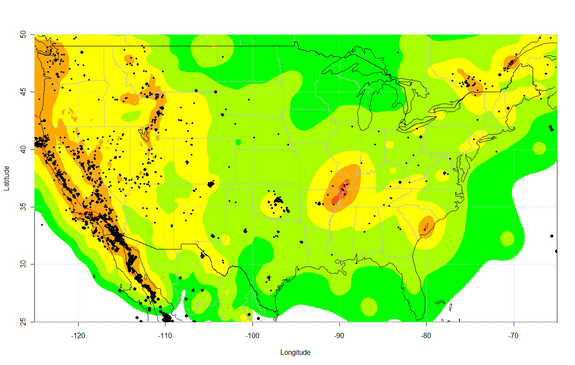
In the Midwest, researchers discovered a warning signal that moderate-sized earthquakes may strike near injection wells, where mining companies dispose of waste fluids. At three sites in Oklahoma, Colorado and Texas, passing seismic waves from faraway earthquakes — the recent massive temblors in Japan, Sumatra and Chile — triggered swarms of small earthquakes. The seismic activity continued until magnitude-4 and magnitude-5 earthquakes struck, such as the large earthquakes near Prague, Okla., in November 2011. [7 Craziest Ways Japan’s Earthquake Affected Earth]
“We’ve been telling our operators for some time that this is one of the warning signs to look for,” said Austin Holland, a seismologist with the Oklahoma Geological Survey who was not involved in the study. “If you see remote triggering of your wells, it’s a clear indication that your faults are right at the failure point. It just took a little tickle, if you will, to trigger the earthquakes.”
In a separate study, researchers documented a clear link between earthquakes and production, or removing and injecting underground fluid, at Southern California’s Salton Sea Geothermal Field power plant. Every 500 million gallons of water pumped out of the ground caused one detectable earthquake per 11 days, according to the report.
“The thing that best predicted the earthquake rate was the net amount of water extracted from the ground,” said Emily Brodsky, lead study author and a seismologist at the University of California, Santa Cruz.
Scientists have long known that geothermal projects can trigger earthquakes, but some communities are wary of the seismic risk. Construction on a geothermal energy plant in Basel, Switzerland, was shut down in 2009 after fluid injection triggered earthquakes up to magnitude 3.4. Brodsky’s study offers a new statistical model for predicting how many earthquakes to expect at a geothermal plant, based on the amount of fluid going in and out of the ground.
“This paper has made a very direct and compelling correlation between the net of fluid out and fluid in and the rate at which these small earthquakes are happening,” said William Ellsworth, a seismologist at the U.S. Geological Survey’s Earthquake Science Center, who was not involved in the study. “This seems like a very promising way of applying this particular statistical model.”
Remotely triggered warnings
Many scientists also suspect a link between mining-related wastewater injection wells and a barrage of earthquakes in the central and eastern United States in the past decade. The surge outpaced natural background trends starting in 2001, according to a review by Ellsworth also published today in Science. But proving a cause-and-effect has been difficult for researchers, who lack the evidence for a slam-dunk case. Outside of California, there are few dense seismic networks to precisely locate small earthquakes, and injection well data is not immediately available.
Discovering earthquake warning signals in the Midwest, before the larger, more damaging temblors, was possible only through a temporary, massive seismic monitoring network called the USArray. The explosion in shale gas exploration also helped, because remote triggering is most common in places with high fluid pressure, such as geothermal fields, hot springs and the estimated 100,000 injection wells in the United States. [Top 10 Alternative Energy Bets]
A quick reminder: Fracking itself doesn’t cause felt earthquakes. Injecting fluids into the ground (as happens with the wastewater from fracking) spawns man-made earthquakes. The added fluids increase pore pressure on a fault’s surface, unclamping the fault and making it easier to slip.
“The fluids are weakening the fault,” said Nicholas van der Elst, a seismologist at Columbia University’s Lamont Doherty Earth Observatory in New York and lead author of the remote-triggering study. More than 50 years of controlled and unintentional experiments have proved the link.
But even with a better seismic network, remotely triggered earthquakes are of limited use as warning signals. First, not all regions with possible man-made earthquakes also had remotely triggered earthquake swarms. Second, only one earthquake every year, on average, is big enough to send seismic waves rippling across Earth’s surface.
“The trouble with using this for forecasting is that the huge earthquakes that are triggering earthquakes are extremely rare,” Frohlich said. “We’ve had three in the last few years, but that’s an unusual rate. In the last 50 years, we’ve only had maybe a dozen earthquakes that big.”
The three sites with earthquake “sirens” were Prague, Okla., Synder, Tex., and Trinidad, Colo. Each saw a spike in seismic activity near injection wells within 24 hours of huge earthquakes in Chile in 2010, Japan in 2011 or Sumatra in 2012. The number of quakes increased until a magnitude-4 or magnitude-5 earthquake hit, includingOklahoma’s strongest recorded earthquake.
“I think this [study] shows that fluid pressure is really driving these earthquakes,” Van der Elst said. “Stress has been increased by the injection of all this fluid in these regions where people have suggested a connection between wells and earthquakes.
“The big implication in this is that remote triggering could act as a stress probe. You could look for remote triggering to anticipate large induced earthquakes,” Van der Elst said.
Better seismic monitoring needed
But well operators are already aware that upticks in seismicity near their injection sites are a warning sign that a larger quake could strike, Holland said. Some companies operate their own seismic networks to monitor wells, he added. “The idea of controlling your injection parameters based on the seismicity you’re observing has been around for 30 or 40 years,” he said.
In his Science review, Ellsworth recommends seismic monitoring of wells to improve understanding of man-made earthquakes and help regulators set seismic activity thresholds that limit injection if there are too many small quakes.
“We need better seismic monitoring so we can see the small earthquakes, and I would also like to have more information about the actual disposal process,” Ellsworth said. “Right now, all that’s required is monthly reporting, and that’s not adequate to build geophysical and geological models of the [earthquake] process.” Regulators developing new laws and reporting requirements also need much more timely and better information, Ellsworth said.
In response to Oklahoma’s recent uptick in earthquakes, the Oklahoma Geological Survey is doubling and modernizing its seismic monitoring network, Holland said.
Email Becky Oskin or follow her @beckyoskin. Follow us @OAPlanet, Facebook & Google+. Original article on LiveScience’s OurAmazingPlanet.