By Micheal Rios, Tulalip News
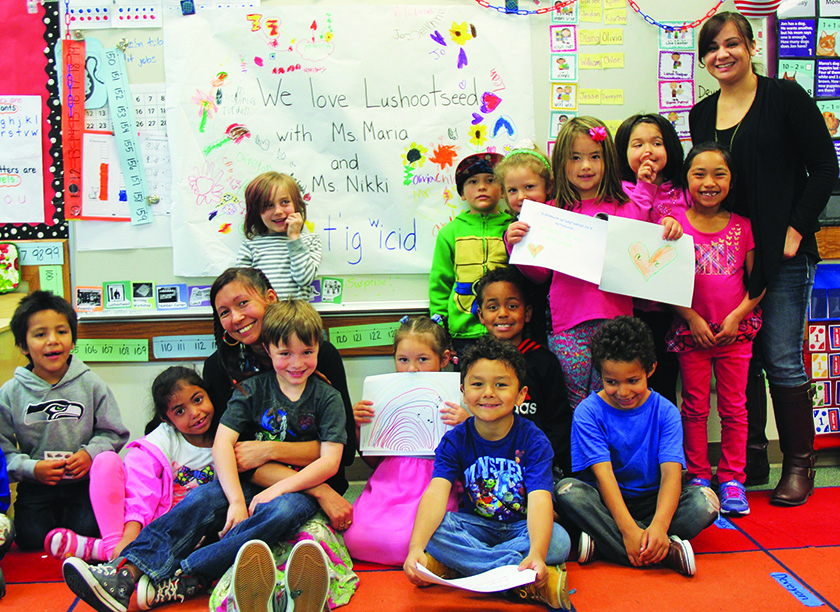
During the pleasantly warm and sunny summer days of July 18-22, the old Tulalip Elementary gymnasium was home to the 21st Annual Lushootseed Day Camp. The camp was open to children age five to twelve who wanted to learn about their culture and Lushootseed language through art, songs, games, weaving and storytelling. Each year the Lushootseed Department teams up with the Cultural Resources Department, along with a select number of very vital community volunteers, to hold two one-week camps. Each camp has openings for up to 50 participants, but this year the demand was so high that 64 kids were signed up and participated in Language Camp week 1.
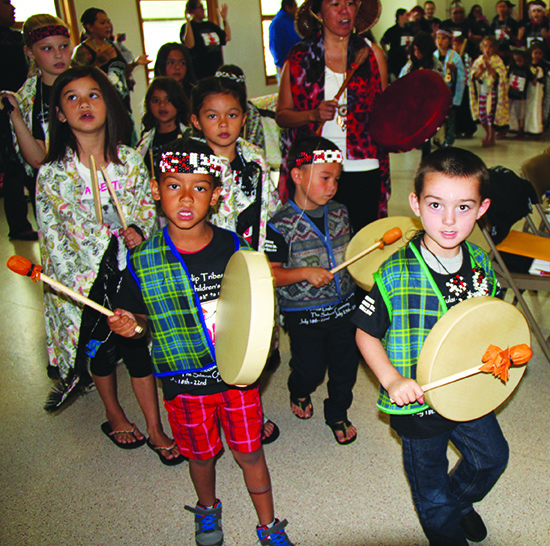
“We are dedicating the 21st Annual Lushootseed Language Camp to Morris Dan and Harriette Shelton-Dover, for their guidance and teachings bringing back the Salmon Ceremony, as well as honoring Stan Jones Sr. “Scho-Hallem” for his decades of leadership and determination to keep the ceremony going,” said Lushootseed language teacher and co-coordinator of the camp, Natosha Gobin. “This year we are recreating the Salmon Ceremony to pass on the teachings to our youth. With the generosity of the Tulalip Tribes Charitable Table, we have received a grant to make regalia for each youth who is signed up for camp. This is exciting, as we will be able to ensure that all the youth who sign up for camp will have the ability to stand up and sing at every opportunity. Vests and drums will be the regalia for the boys, while the girls’ regalia will be shawls and clappers.”
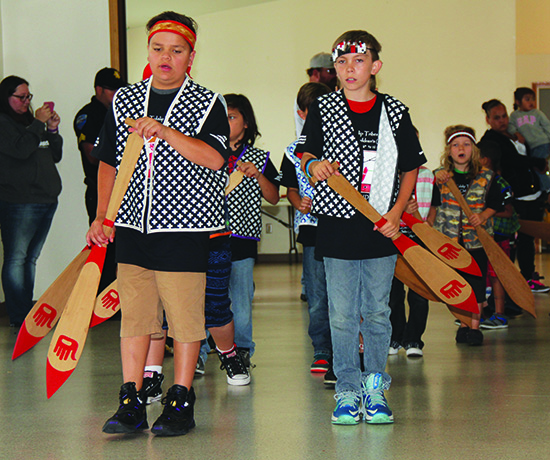
Using the 1979 Salmon Ceremony video to help pass on the earliest teaching of what is still practiced today, the young campers learned a selection of highlighted songs and dances. The lessons learned each day during Language Camp were based on the teachings of the Salmon Ceremony by way of songs and dances, traditional teachings, language, art, weaving, and technology. The goal this year was to provide our youth with some basic regalia along with the knowledge and ability to sing and dance. Staffers hope the youth that have participated have the teachings and experience needed so they will stand up and sing at every opportunity.
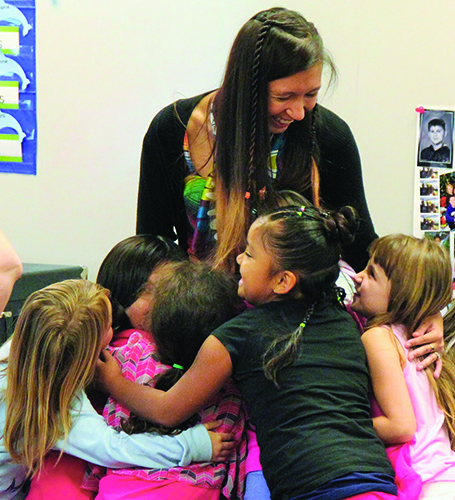
With the emphasis of honoring the past and impacting the future with education and practice of Salmon Ceremony, there was a renewed sense of excitement and vigor to both the teachers and bright, young minds who participated. There was so much to do and prepare for that the parents of each camper were also called upon to participate in create long-lasting memories while working with their kids and fellow community members to help make regalia.
During the evening of Tuesday, July 19 the parents came through in a big way. The parents and guardians joined their kids in the gymnasium and were guided on how to make the drums and clappers. There were lots of laughs and stories shared as the evening went on and slowly, but surely every camper was assured of hand-made regalia.
“This is what we wanted to bring back; families coming together to spend some time working on the drums and clappers, lots of smiles, and most importantly lots of happy kids,” stated Natosha after the evening of regalia making concluded. “A huge thank you to the parents, aunties, uncles, grandparents, siblings and cousins who come out tonight to make sure every child would have a drum or clapper. I know our ancestors are watching over us all and proud the teachers are still being passed on.”
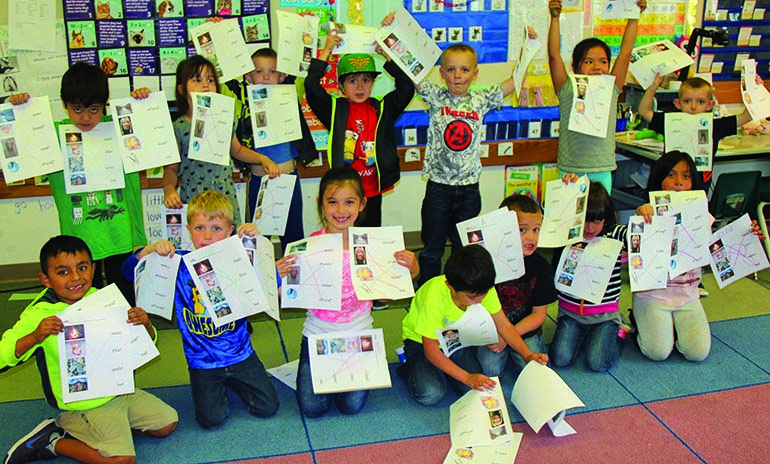
Throughout the duration of camp, the children participated in seven different daily activities. The following list is what each child accomplished throughout the week:
- Art – Salmon bracelets, Salmon hands, paddle necklaces.
- Weaving – Pony Bead loom beading, small raffia baskets.
- Songs and Dances – Welcome Song, Eagle Owl BlueJay Song, Snohomish Warrior Song.
- Traditional Teachings – Salmon Ceremony videos, traditional stories, realia experience in traditional story and science face of how Salmon migrate.
- Games – Various games and playground time.
- Language – letter sounds, Salmon Ceremony key words, Lushootseed workbook.
- Technology – children learned and practiced Lushootseed materials related to Salmon Ceremony using the Nintendo DSi handheld games created by Dave Sienko.
The closing ceremony for week one’s camp was held on Friday, July 22 in the Kenny Moses Building. The joyous, young play-performers made their debut to a large community attendance, as family and friends came out in droves to show their support.
“The young ones continue to honor our ancestors by learning their songs and words. It fills my heart with so much joy to watch them speak our language and perform the dances of Salmon Ceremony,” marveled ceremonial witness Denise Sheldon.
After the youth performed their rendition of Salmon Ceremony and the ceremonial witnesses had shared a few words, there was a giveaway. The camp participants gave handmade crafts to the audience members, which preceded a salmon lunch that everyone thoroughly enjoyed.
Reflecting on the conclusion of this year’s 21st Annual Language Camp week one, Natosha Gobin beamed with pride, “Week one has come to an end, but it is truly just the beginning of our youth rising up! The fire has been lit and they will be the ones to keep it burning. I can’t say it enough, how thankful we are for the parents that sign their youth up to participate. Shout out to the volunteers who mentored our young Language Warriors and to the staff who prepped and taught the lessons, and those who did all the behind the scenes work. Thank you to each and every person who made this week’s camp a success.”
For any questions, comments or to request Lushootseed language materials to use in the home, please contact the Lushootseed Department at 360-716-4499 or visit www.TulalipLushootseed.com