By Betsy Hammond | betsyhammond@oregonian.com
Email the author | Follow on Twitter
on January 22, 2014 The Oregonian
Children who are members of Oregon Indian tribes fare extremely poorly in Oregon schools, in part because so many of them miss a lot of school, a new study shows.
They also suffer academically because 30 percent are enrolled in the state’s worst performing schools, compared with 7 percent of students statewide who attend schools with bottom-tier results, the study found.
Only about 40 percent of Oregon students who are official members of an Oregon tribe can do math at grade level, and only about half read at grade level in elementary and middle school, the study found.
And just 59 percent of tribal members in the class of 2011 earned a diploma within five years of starting high school, compared with 72 percent of all Oregon students.
“It is disturbing to see that so many tribal member kids all across our state are not getting an effective education,” said Kathleen George, director of the Spirit Mountain Community Fund. “It feels like they are out of sight and out of mind.”
The outcomes are much worse than has generally been understood because Oregon tracks students as Native American if they or their parents say they are. But only about 5 percent of those students are enrolled members of an Oregon tribe, the study found.
Compared with tribal members, students the state tracks as Native American are less likely to be in special education, more likely to live in a city or a suburb, less likely to move during the school year and less likely to get suspended from school.
The study was paid for by the Spirit Mountain Community Fund, the philanthropic arm of the Confederated Tribes of Grand Ronde. It was conducted by ECONorthwest and overseen by the Chalkboard Project.
Seven of Oregon’s nine federally recognized tribes and tribal confederations took part: the Cow Creek Band of Umpqua, the Burns Paiute, the Klamath, the Grand Ronde, the Siletz, the Umatilla and the Warm Springs.
Together, those tribal groups have about 3,200 students in Oregon public schools, or about 250 per grade.
That compares with about 67,000 students statewide whose school records indicate they are solely or partly Native American.
Two of Oregon’s smaller tribes did not participate in the study: the Coquille and the Confederated Tribes of Coos, Lower Umpqua and Siuslaw.
ECONorthwest and the Chalkboard Project have a special arrangement with the Oregon Department of Education that gives the research firm access to otherwise confidential student records.
Leaders of the seven tribes provided the department with the names of their school-age members. The department in turn informed ECONorthwest researchers which Oregon student ID numbers belong to an enrolled tribal member.
Using their large database of student records, researchers then were able to compile an unprecedented statistical portrait of how tribal young people fare in Oregon public schools.
Ramona Halcomb, director of education at the Confederated Tribes of the Umatilla Indian Reservation, said those findings “are not what we were hoping for, but they’re useful so we know how far we need to go to get to our goal.”
During 2011-12, one of every three students from an Oregon tribe was “chronically absent,” meaning the student missed 10 percent of school days or more, the study found.
Students who miss that much school are unlikely to ever read or do math at grade level or to earn diplomas, other studies have shown.
The 33 percent chronic absentee rate among tribal members was much worse than the high statewide chronic absentee rate of 19 percent and the 23 percent chronic absentee rate for all students who identify as Native American, the study found.
Authors of the study are urging tribes and state policymakers to consider working with foundations or nonprofits to find a strategy to cut tribal children’s chronic absenteeism rate in half. That would likely require changes in both schools and tribal households, the study said.
George said she and other tribal leaders plan to follow through.
“We need to help foster a change in culture to help our children understand that showing up in school every day is the path to success in school and later in life,” she said. She said they will work “to help children see school as a place that is important, that is a path to success and where they feel valued and see the value for them.”
Tribal children are concentrated in Oregon’s worst performing schools, the study found.
All three schools attended by students who live on or near the Warm Springs reservation, Warm Springs Elementary, Jefferson County Middle School and Madras High, rank in the bottom 5 percent of Oregon Schools based on their 2011-12 test scores and graduation rates. So does Chiloquin Elementary, which serves the tiny town where the Klamath Tribes are based.
George said she was alarmed to learn that tribal children are five times more likely than other children to attend a school with rock-bottom results, many of them in rural parts of Oregon. “That is an important finding that we need to address. There is no denying that part of the solution must be to bring change to these rural schools and help all the children in these rural schools.”
One surprisingly good outcome for tribal youths: Members of Oregon tribes who graduate from an Oregon high school enroll in college at about the same rate as Oregon students as a whole. Roughly 60 percent of both groups enroll in a community college or four-year college within 16 months of finishing high school, the study found.
Other findings about students who are members of Oregon tribes include:
- Almost half live in rural areas and another one-third live in small towns. Only 20 percent live in a city or suburb.
- 17 percent are in special education, compared with 13 percent of Oregon students as a whole.
- 11 percent were suspended from school, compared with 7 percent of Oregon students as a whole.
- 75 percent qualify for subsidized school meals, meaning they live in low-income families.
- 11 percent changed schools at least once during the 2011-12 school year.
- Only 46 percent of tribal members in middle school passed the state reading test, but 69 percent of tribal members in high school did.
— Betsy Hammond


















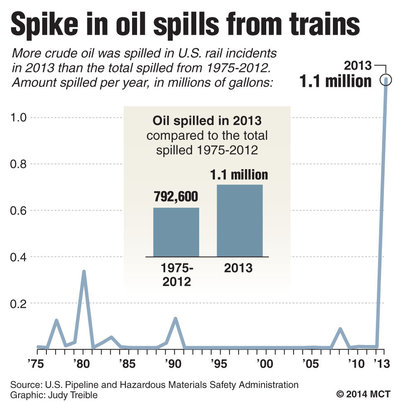 But until just a few years ago, railroads weren’t carrying crude oil in 80- to 100-car trains. In eight of the years between 1975 and 2009, railroads reported no spills of crude oil. In five of those years, they reported spills of one gallon or less.
But until just a few years ago, railroads weren’t carrying crude oil in 80- to 100-car trains. In eight of the years between 1975 and 2009, railroads reported no spills of crude oil. In five of those years, they reported spills of one gallon or less.