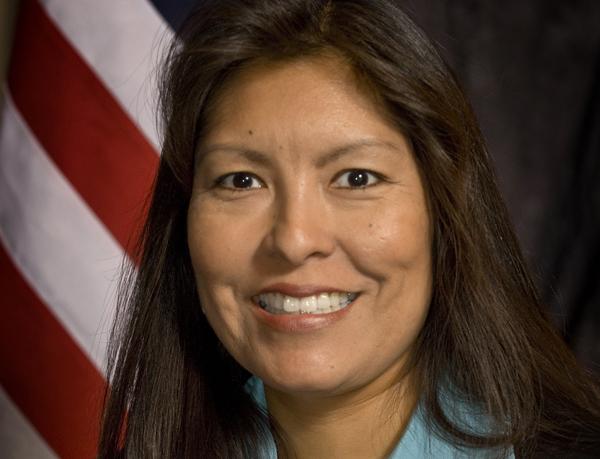
After a tenuous year of leading the Senate Committee on Indian Affairs, Sen. Maria Cantwell (D-Washington) has confirmed that she is moving on.
Following weeks of speculation that she would step down to lead the Small Business Committee after a leadership shuffle among Senate Democrats following Sen. Max Baucus’ (D-Montana) retirement, Cantwell made her intentions clear at a January 29 hearing in Washington, saying it has been a pleasure to serve alongside vice-chair John Barrasso (R-Wyoming) and to work with current Assistant Secretary – Indian Affairs Kevin Washburn.
“It has been a smooth working process,” Cantwell assessed of her work relationship with Barrasso. “We will certainly appreciate working with you again in the future.”
Reid Walker, a spokesman for the senator, said after the hearing that she will remain on SCIA as a member “and remains committed to Indian country.”
Cantwell, while praised as the first female chair of SCIA, has been criticized by some tribal leaders and advocates for not holding as many hearings and for not pushing for as much pro-tribal legislation as immediate past SCIA leaders by this point in their tenures.
Mary Pavel, Cantwell’s staff director and chief counsel, has held several listening sessions with tribal leaders and citizens, but these have not translated into firm action on many economic and social issues facing tribes today.
Pavel told Indian Country Today Media Network in an interview at the beginning of Cantwell’s term in 2013 that she expected the senator would be a strong leader of SCIA, which is not exactly the perception that many tribal leaders currently have of Cantwell’s one year in the position, although Ron Allen, chairman of the Jamestown S’Klallam Tribe in Cantwell’s home state of Washington, said she has done “a great job on behalf of Indian country” in his testimony before the committee on January 29. Tribal leaders from Cantwell’s region have generally been more pleased with her leadership than others.
In the weeks before the Small Business Committee chairmanship opened up, Cantwell had been working behind the scenes at tackling one of the major issues facing Indian country—a legislative fix to the controversial 2009 Supreme Court Carcieri decision that called into question the Department of the Interior’s ability to take lands into trust for tribes recognized by the federal government after 1934.
But Cantwell’s Carcieri legislation was mired in conflict before even getting out of the starting gate, since it was not drafted with wide consultation from tribal leaders. It called for a fix that would exclude the Narragansett Tribe of Rhode Island, and it made modifications to rules that would make gaming impossible or more difficult for some tribes. Many tribes and Indian organizations have argued that land-into-trust policy should not be tied to gaming policy, as they are distinct issues.
According to sources familiar with Cantwell’s effort on the Carcieri draft legislation, she worked with Sen. Dianne Feinstein (D-Calif.) on ideas involving historical connections tests for tribes that want to pursue off reservation gaming. Feinstein has long been controversial in Indian country for her desire to limit tribal gaming, especially in California. In a sign of their closeness, Cantwell sat next to Feinstein at the president’s January 28 State of the Union address, and they have introduced joint legislation in the past. Still, Feinstein’s office insists the senator did not play a role in drafting the legislation.
Tribal leaders who have seen the draft Carcieri legislation have generally let their displeasure with Cantwell’s work here be known, and the legislation is widely considered to be stalled with her moving on from the leadership.
Cantwell’s staff is well aware of the difficulties, but they say the senator has not given up. “Several ideas are being considered with input from multiple stakeholders, and more work needs to be done,” said Walker. “She and the committee remain committed to finding a solution.”
The Carcieri discussions and other issues within SCIA have been tense of late, and there were recent indications that the general tension of the atmosphere was affecting staffers there when Denise Desiderio, a deputy staff director at SCIA, decided to leave after five years with the committee. She has long told colleagues that she loved working there, so her decision was one indication of the difficulties surrounding Cantwell’s tenure, according to sources close to Desiderio.
A major highlight of Cantwell’s leadership was the passage of the reauthorization of the Violence Against Women Act in 2013 that included strong tribal jurisdictional provisions for prosecuting non-Indian offenders on reservations. The senator strongly supported that legislation, and she helped Indian advocates make their voices heard on the issue. She’s also been strong on forcing the federal government to pay contract support costs to tribes, and she has played a role in holding up Indian Health Service Director Yvette Roubideaux’ re-nomination to the position due to tribal concerns.
With Cantwell making her intentions to exit SCIA known, all eyes now turn to Sen. Jon Tester (D-Montana), who will take on the chairmanship, Senate sources have confirmed.
Tester, who has served on the committee since his first term in Congress that started in 2007, has been angling for the position with support from Senate colleagues, including the retiring Baucus. Other contenders were Sen. Tim Johnson (D-S.D.), but he is retiring from Congress at the end of this year, and Sens. Tom Udall (D-N.M.) and Al Franken (D-Minn.) were also interested, according to Senate sources.
Tester, with the strong backing of the tribes in his home state, ended up with the gavel, and he is quickly signaling his intentions to be a proactive chairman. In mid-January, he introduced legislation that would amend the Elementary and Secondary Education Act of 1965 to provide increased federal financial support to Native American language programs at American Indian-focused schools. And on January 30, he provided the congressional response to the annual State of the Indian Nations address hosted by the National Congress of American Indians. He’s also been meeting behind-the-scenes with many tribal leaders and advocates.
“I serve on the Senate Committee on Indian Affairs—we work hard, and the accomplishments are many, from the Native American protections in the Violence Against Women Act to the Indian Health Care Improvement Act to water settlements to my work with veterans to the Tribal Law and Order Act to NAHASDA,” Tester told ICTMN in a 2012 interview. “I am very proud of my record. I also visit every reservation in Montana every year.”
Read more at http://indiancountrytodaymedianetwork.com/2014/01/30/under-tribal-scrutiny-cantwell-exiting-scia-tester-take-charge-153334










![The Intricate Beadwork of Jackie Larson Bread [10 Pictures]](https://www.tulalipnews.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/01/jackie-bread-featured-50x50.jpg)