Cassandra Profita, OPB
An environmental group is calling for a major expansion in habitat protection for Puget Sound’s killer whales.
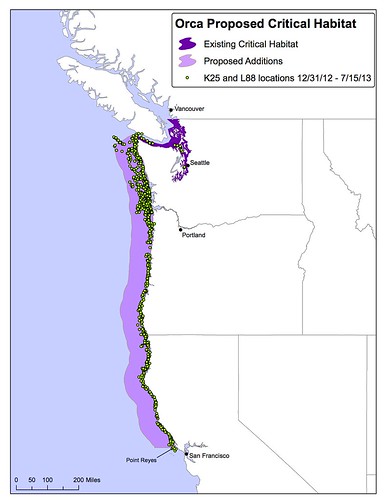
Research shows the endangered orcas that live in Puget Sound in the summer are venturing up and down the West Coast in the winter to forage for food. Scientists tracking these southern resident orcas have followed the whales as far north as Alaska and as far south as Monterey, Calif.
Given these findings, the Center for Biological Diversity says the whales need a lot more habitat protection than they have now. The group filed a petition Thursday with the National Marine Fisheries Service to expand protected habitat for the whales from Puget Sound to a large swath of ocean area off the coasts of Washington, Oregon and Northern California.
“They need to protect all of their habitat — not just where the whales hang out in the summer,” says Sarah Uhlemann of the Center for Biological Diversity.
Protected habitat for species listed under the Endangered Species Act, known as “critical habitat,” comes with restrictions on actions taken by the federal government that might threaten the species’ survival.
Uhlemann says those restrictions would apply to federal decisions on salmon fishing, port expansions and other coastal developments. That would mean any time the federal government decides to do anything -– say the Navy decides to practice some sonar or an agency is deciding whether to permit a port expansion — the government would have to fully consider environmental impacts.
“Not only on the whale but also on its habitat –- and if the impacts are too large they have to stop and mitigate, or lessen what those impacts are,” Uhlemann said.
Lynne Barre is a marine biologist and manager in Seattle with the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. She said the federal government was already considering an expansion in habitat protections for southern resident orcas as its tagging research program has revealed more about where the whales are feeding.
“Our knowledge of their habitat in the ocean is increasing,” Barre said. “Gathering additional information about their coastal habitat was one of the priorities we identified when we listed the orcas for protection under the Endangered Species Act in 2005.”
The orcas face threats from a lack of available food because they primarily survive on salmon, Barre said. They also accumulate high levels of contaminants such as flame retardants, legacy pesticides and industrial pollutants that can impact their immune systems. Orcas are acoustic animals that use sound to communicate with each other and find prey, she said, so underwater noises from vessels and other activities pose another threat to the whales.
The existing critical habitat protections in Puget Sound require evaluations of the impacts to whales from pollution discharges, ship passage and construction activities such as pile-driving, Barre said. Federal regulators will have 90 days to decide whether to review the Center for Biological Diversity’s petition to expand the area where those kinds of protections apply.